Because the power level is proportional to the bandwidth twice the bandwidth level gives twice the power level 3db and ten times the bandwidth gives ten times the power level 10db.
Thermal noise floor 174.
A good model should capture the drain noise current accurately in all.
Analyzing noise in general can be difficult as there are a variety of intrinsic noise sources and these intrinsic noise sources are unique to different systems.
Thermal noise spectrum is gaussian in shape.
It is measured in noise power units of dbm or watt or noise voltage.
Thermal noise power and voltage equation.
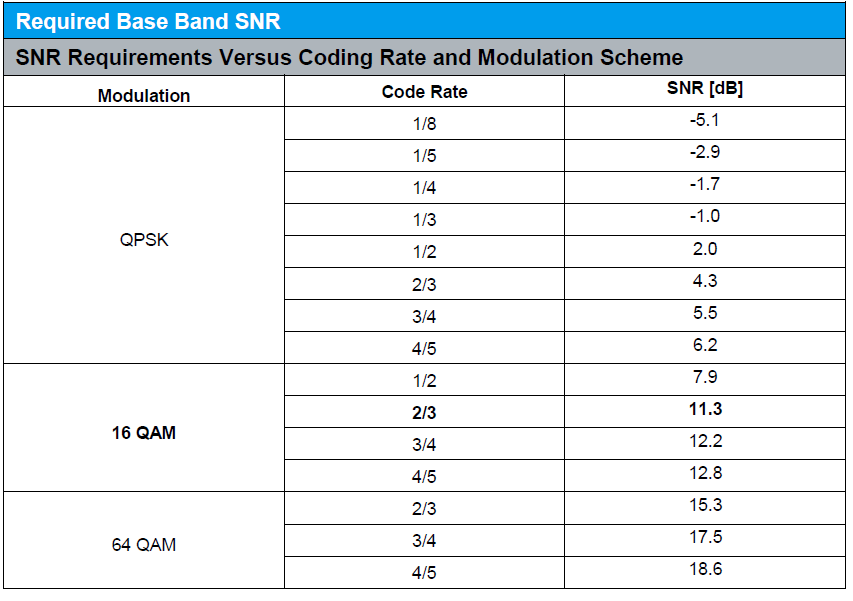
1 hz noise floor equates to a noise power of 174 dbm so a 1 khz bandwidth would generate 174 10 log 10 1 khz 144dbm of noise power the noise is thermal noise johnson noise.
When drift current dominates the thermal noise is a function of the channel conductance whereas in moderate and weak inversion the diffusion component gives rise to shot noise.
Johnson nyquist noise thermal noise johnson noise or nyquist noise is the electronic noise generated by the thermal agitation of the charge carriers usually the electrons inside an electrical conductor at equilibrium which happens regardless of any applied voltage thermal noise is present in all electrical circuits and in sensitive electronic equipment such as radio receivers can.
If we look at the normalized b 1 hz bandwidth noise floor equation we have.
Noisefloor 10 log10 k t b 10 log10 1 38 10 23 290 1 hz.
Relative to the bandwidth we can use the reference level of 174 dbm hz and simply multiply it by the actual bandwidth of the radio channel.
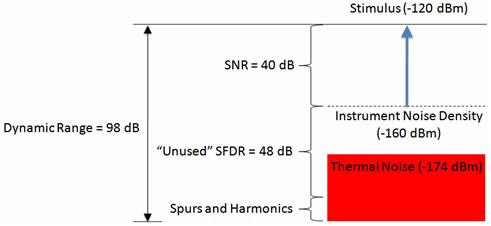
Mds 10log kto 1e3 nf 10log bw snr the equation above indicates several ways in which the minimum detectable signal of a receiver can be improved.
Let s calculate the thermal noise floor of the 200 khz.
It is then easy to relate this to other bandwidths.
This noise gained its various names because this noise was first detected and measured by john b.
Noise power of 174 dbm hz is the reference for any noise power calculation when designing rf systems working at room temperature.
The noise resulting from thermal agitation of electrons is referred as thermal noise.
Thermal noise in a 50 ω system at room temperature is 174 dbm hz.
Following equation or formula is used for thermal noise power and voltage calculator.
To convert the noise power to db watts use 10 times the log of the noise power in watts.
Johnson in 1926 and later explained by harry nyquist both were bell labs and working together.
In the absence of any broadband noise sources 1 f noise or brownian noise the minimum noise level you can hope to measure in an electronic system is the thermal noise floor.